# 【死磕 Spring】—— IoC 之深入分析 PropertyOverrideConfigurer
**本文主要基于 Spring 5.0.6.RELEASE**
摘要: 原创出处 http://cmsblogs.com/?p=todo 「小明哥」,谢谢!
作为「小明哥」的忠实读者,「老艿艿」略作修改,记录在理解过程中,参考的资料。
------
在文章 [《【死磕 Spring】—— IoC 之深入分析 BeanFactoryPostProcessor》](http://svip.iocoder.cn/Spring/IoC-BeanFactoryPostProcessor) 中提到,BeanFactoryPostProcessor 作用与 BeanDefinition 完成加载之后与 Bean 实例化之前,是 Spring 提供的一种强大的扩展机制。它有两个重要的子类,一个是 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,另一个是 PropertyOverrideConfigurer ,其中 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 允许我们通过配置 Properties 的方式来取代 Bean 中定义的占位符,而 **PropertyOverrideConfigurer** 呢?正是我们这篇博客介绍的。
> PropertyOverrideConfigurer 允许我们对 Spring 容器中配置的任何我们想处理的 bean 定义的 property 信息进行覆盖替换。
这个定义听起来有点儿玄乎,通俗点说,就是我们可以通过 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 来覆盖任何 bean 中的任何属性,只要我们想。
# 1. 使用
PropertyOverrideConfigurer 的使用规则是 `beanName.propertyName=value`,这里需要注意的是 `beanName.propertyName` 则是该 bean 中存在的属性。
## 1.1 示例一
依然使用以前的例子,`Student.class`,我们只需要修改下配置文件,声明下 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 以及其加载的配置文件。如下:
```
classpath:application.properties
```
- 指定 student 的 `name` 属性值为 `"chenssy"` 。
- 声明 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 加载的文件为 `application.properties`,内容如下:
```
student.name = chenssy-PropertyOverrideConfigurer
```
- 指定 beanName 为 `student` 的 bean 的 `name` 属性值为 `"chenssy-PropertyOverrideConfigurer"` 。
测试打印 `student` 中的 `name` 属性值,代码如下:
```
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("student name:" + studentService.getName());
```
运行结果为:
[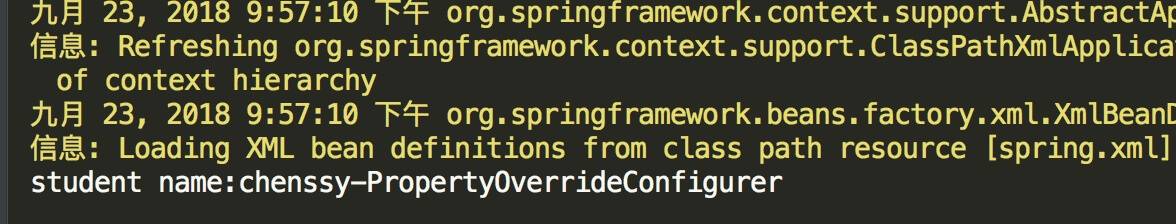](http://static.iocoder.cn/15377119278769.jpg)
从中可以看出 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 定义的文件取代了 bean 中默认的值。
## 1.2 示例二
下面我们看一个有趣的例子,如果我们一个 bean 中 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 和 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 都使用呢?那是显示谁定义的值呢?这里先简单分析下:如果PropertyOverrideConfigurer 先作用,那么 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 在匹配占位符的时候就找不到了,**如果 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 后作用,也会直接取代 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 定义的值,所以无论如何都会显示 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 定义的值**。是不是这样呢?看如下例子:
xml 配置文件调整如下:
```
classpath:application1.properties
classpath:application2.properties
```
- 指定 .PropertyOverrideConfigurer 加载文件为 `application1.properties` 。配置文件如下:
```
student.name = chenssy-PropertyOverrideConfigurer
```
- PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 加载文件为 `application2.properties` 。配置文件如下:
```
studentService.name = chenssy-PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
```
- `student` 的 `name` 属性使用占位符 `${studentService.name}`。
测试程序依然是打印 name 属性值,运行结果如下:
[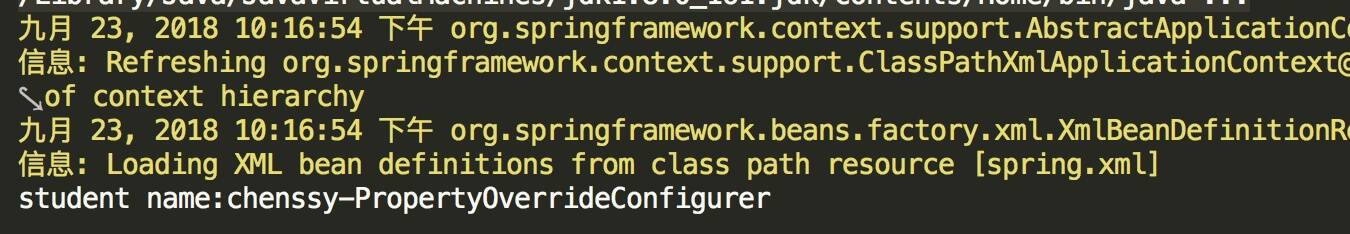](http://static.iocoder.cn/15377127284347.jpg)
所以,上面的分析没有错。下面我们来分析 **PropertyOverrideConfigurer 实现原理**。
其实如果了解 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 的实现机制的话,那么 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 也不难猜测:加载指定 Properties,迭代其中的属性值,依据 `“.”` 来得到 `beanName`(`split(".")[0]`),从容器中获取指定的 BeanDefinition,然后得到 `name` 属性,进行替换即可。
# 2. 实现原理
UML 结构图如下:
[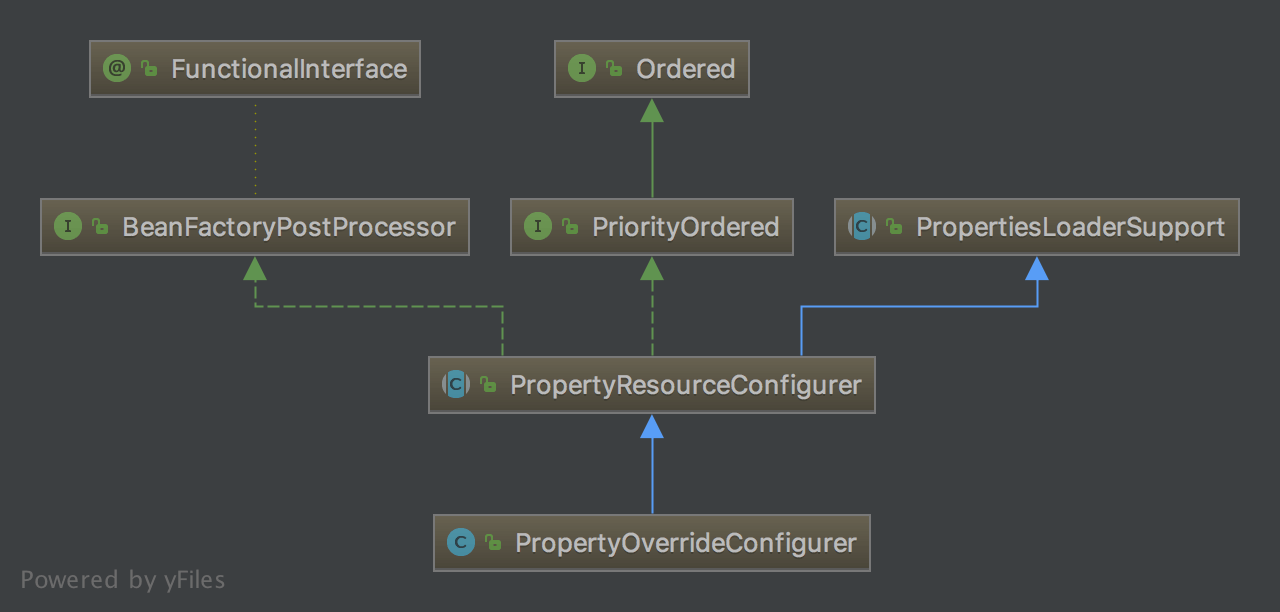](http://static.iocoder.cn/spring-201809231001.png)spring-201809231001
与 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 一样,也是继承 PropertyResourceConfigurer,我们知道 PropertyResourceConfigurer 对 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 `#postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)` 方法提供了实现,在该实现中它会去读取指定配置文件中的内容,然后调用 `#processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, Properties props)` 方法。该方法是一个抽象方法,具体的实现由子类来实现,所以这里我们只需要看 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 中 `#processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, Properties props)` 方法的具体实现,代码如下:
```
// PropertyOverrideConfigurer.java
@Override
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, Properties props)
throws BeansException {
// 迭代配置文件中的内容
for (Enumeration names = props.propertyNames(); names.hasMoreElements();) {
String key = (String) names.nextElement();
try {
processKey(beanFactory, key, props.getProperty(key));
} catch (BeansException ex) {
String msg = "Could not process key '" + key + "' in PropertyOverrideConfigurer";
if (!this.ignoreInvalidKeys) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(msg, ex);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(msg, ex);
}
}
}
}
```
- 迭代 `props` 数组,依次调用 `#processKey(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory factory, String key, String value)` 方法,代码如下:
```
// PropertyOverrideConfigurer.java
/**
* The default bean name separator.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_BEAN_NAME_SEPARATOR = ".";
/**
* Bean 名字的分隔符
*/
private String beanNameSeparator = DEFAULT_BEAN_NAME_SEPARATOR;
/**
* Contains names of beans that have overrides.
*/
private final Set beanNames = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16));
protected void processKey(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory factory, String key, String value)
throws BeansException {
// 判断是否存在 ".",即获取其索引位置
int separatorIndex = key.indexOf(this.beanNameSeparator);
if (separatorIndex == -1) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Invalid key '" + key +
"': expected 'beanName" + this.beanNameSeparator + "property'");
}
// 得到 beanName
String beanName = key.substring(0, separatorIndex);
// 得到属性值
String beanProperty = key.substring(separatorIndex+1);
this.beanNames.add(beanName);
// 替换
applyPropertyValue(factory, beanName, beanProperty, value);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Property '" + key + "' set to value [" + value + "]");
}
}
```
- 获取分割符 `“.”` 的索引位置,得到 `beanName` 以及相应的属性,然后调用 `#applyPropertyValue(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory factory, String beanName, String property, String value)` 方法,代码如下:
```
// PropertyOverrideConfigurer.java
protected void applyPropertyValue(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory factory, String beanName, String property, String value) {
// 获得 BeanDefinition 对象
BeanDefinition bd = factory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
BeanDefinition bdToUse = bd;
while (bd != null) {
bdToUse = bd;
bd = bd.getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}
// 设置 PropertyValue 到 BeanDefinition 中
PropertyValue pv = new PropertyValue(property, value);
pv.setOptional(this.ignoreInvalidKeys);
bdToUse.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(pv);
}
```
- 从容器中获取 BeanDefinition ,然后根据属性 `property` 和其值 `value` 构造成一个 PropertyValue 对象,最后调用 `#addPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv )` 方法。PropertyValue 是用于保存一组bean属性的信息和值的对像。代码如下:
```
// MutablePropertyValues.java
public MutablePropertyValues addPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.propertyValueList.size(); i++) {
PropertyValue currentPv = this.propertyValueList.get(i);
// 匹配
if (currentPv.getName().equals(pv.getName())) {
// 合并属性
pv = mergeIfRequired(pv, currentPv);
// 覆盖属性
setPropertyValueAt(pv, i);
return this;
}
}
// 未匹配到,添加到 propertyValueList 中
this.propertyValueList.add(pv);
return this;
}
```
- 添加 PropertyValue 对象,替换或者合并相同的属性值。整个过程其实与上面猜测相差不是很大。
# 3. 小结
至此,PropertyOverrideConfigurer 到这里也就分析完毕了。最后看下 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 和 PropertyOverrideConfigurer 整体的结构图:
[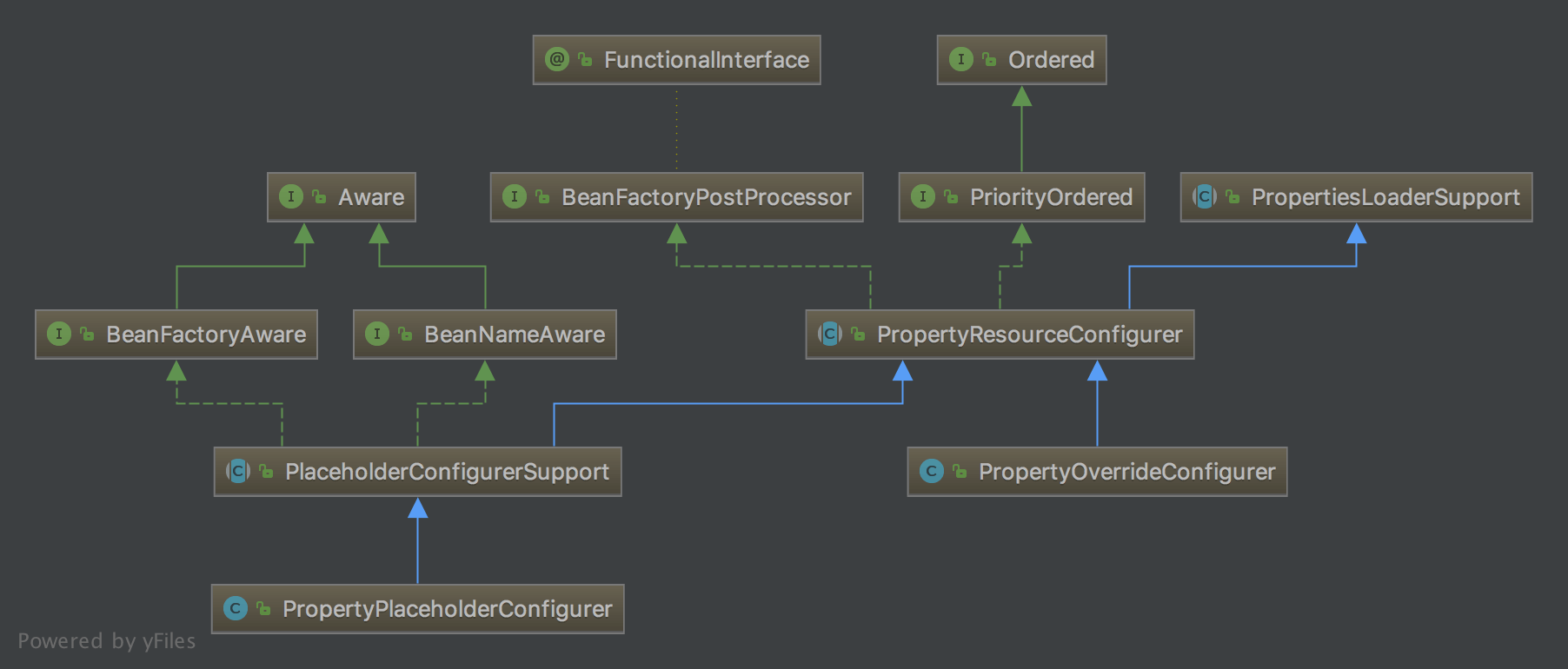](http://static.iocoder.cn/spring-201809231002.png)spring-201809231002